Revolutionizing Gene Therapy with Innovative mRNA Delivery
Written on
Understanding the RNA Family
In recent years, terms like genome, gene, and DNA have become commonplace in discussions about biology. At the core of our cells lies the genome, a comprehensive collection of genes essential for our development and functionality, all encoded in the four-letter language of DNA.
However, this narrative is often overly simplified. While genes constitute about 2% of our genome, the remaining 98% consists of non-coding DNA, which includes remnants of obsolete genes, repetitive sequences, and even traces of ancient viral integrations known as endogenous retroviruses (ERVs).
To grasp the complete picture, we must introduce a vital player: RNA, the multi-functional counterpart to DNA. For a gene within the DNA to synthesize a protein, it must first be transcribed into messenger RNA (mRNA), which is then translated into a series of amino acids, forming the desired protein.
The Versatile Role of RNA
RNA is far from a one-dimensional molecule; it exists in various forms, each serving distinct functions. Among the prominent types are:
- Messenger RNA (mRNA): Transcribes the information from DNA.
- Transfer RNA (tRNA): Delivers amino acids to ribosomes for protein synthesis.
- Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): Forms the core of ribosomes, facilitating the assembly of proteins.
Historically, DNA has garnered more attention due to its role as the blueprint for life, yet RNA's importance is increasingly recognized, particularly through innovations like mRNA vaccines.
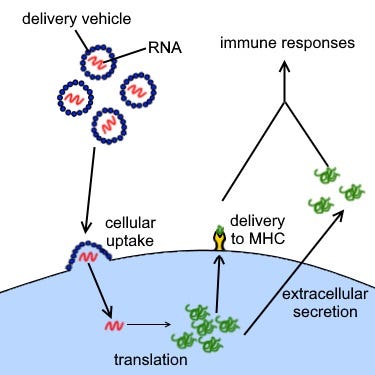
mRNA Vaccines: A Case Study
The emergence of mRNA vaccines during the COVID-19 pandemic exemplifies RNA's potential. Both the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna vaccines utilize mRNA technology, which offers several advantages: unlike traditional vaccines, they don't require a fragment of the pathogen, and the process of producing mRNA is quicker, more cost-effective, and less error-prone.
But why not opt for DNA in vaccine development? While that's an option, mRNA holds a distinct advantage by bypassing a transcription step that DNA must undergo within the nucleus, allowing for faster protein production and thereby a more efficient immune response.
Innovative Approaches in Gene Therapy
RNA is also making strides in gene therapy. One of the initial approaches, RNA silencing, employs a custom RNA strand to bind to specific mRNA, thereby modifying gene expression. Another technique leverages mRNA to stimulate cells to produce a healthy version of malfunctioning proteins.
However, a significant challenge remains: delivering RNA to the targeted cells. Recent research has identified an innovative solution using the RNA itself.
Researchers discovered that PEG10, a viral remnant integrated into our genome, can encapsulate itself within its RNA. By pinpointing the mRNA sequences that PEG10 utilizes for this self-packaging, they successfully introduced additional mRNA sequences within these signals, ensuring their effective delivery.
To enhance this system, researchers incorporated fusogens—surface proteins that enable binding to specific cell types—into the PEG10 capsule. This novel system, dubbed Selective Endogenous Encapsidation for Cellular Delivery (SEND), has shown promise in both mouse and human cell cultures.
SEND is not only customizable but also targets specific cells without triggering immune responses, due to its reliance on sequences already present in the body. The researchers concluded that SEND represents a modular platform with potential for efficient therapeutic delivery.
Next Steps for SEND
This groundbreaking development is just the beginning for SEND, with forthcoming animal trials set to further evaluate its efficacy.
The first video titled "mRNA Translation (Advanced)" offers an in-depth look at the intricacies of mRNA translation, providing insights into its advanced applications in biotechnology.
The second video, "mRNA Translation (Basic)," serves as an introductory overview, explaining the fundamental processes involved in mRNA translation and its significance in gene expression.