Innovative Solutions for a Sustainable Food Future
Written on
Chapter 1: The Consumer's Perspective
In the United States, only a mere 3% of consumers view meat as a significant contributor to climate change. This raises the question: Are we addressing an issue that consumers remain largely unaware of?
This paragraph will result in an indented block of text, typically used for quoting other text.
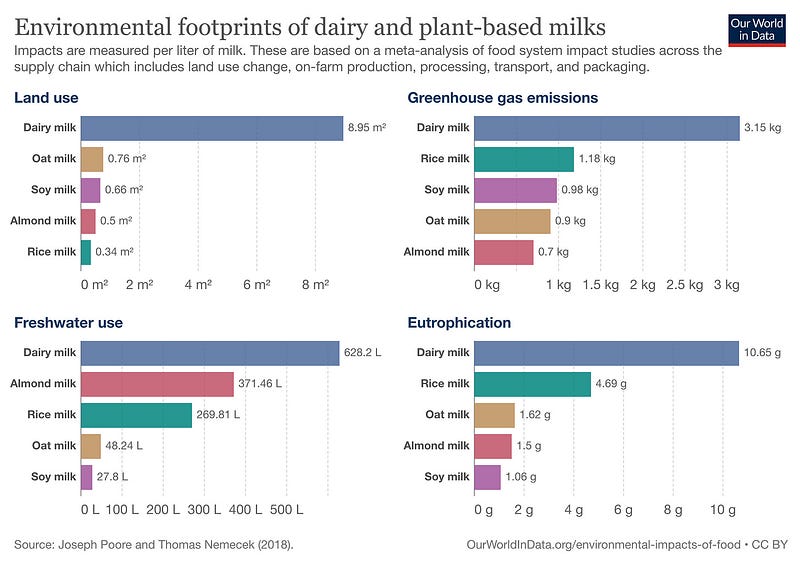
Section 1.1: The Environmental Impact of Dairy
Plant-based milk alternatives present a more environmentally friendly option compared to traditional dairy milk. According to data from Our World in Data, dairy farming requires extensive land for raising livestock and producing feed, which can lead to deforestation and loss of biodiversity. In contrast, producing plant-based milk necessitates approximately nine times less land. Moreover, the dairy industry is infamous for its excessive water usage, which not only strains freshwater resources but also contributes to water pollution through manure runoff and the use of fertilizers and pesticides.

Section 1.2: Singapore's Approach to Food Security
Singapore is pioneering efforts in the alternative protein market, with local startups developing plant-based and cultivated meat products that are making their way into restaurants across Asia and the Middle East. This innovation is crucial as it addresses the vulnerabilities of traditional agriculture, which can be impacted by supply chain disruptions and environmental challenges. The city-state has set an ambitious target to produce 30% of its own food by 2030, leveraging alternative proteins to bolster food security.
The World BioEconomy Forum Declaration 2023 discusses the importance of a sustainable bioeconomy in addressing global food challenges and climate change.
Chapter 2: Innovations in Agriculture
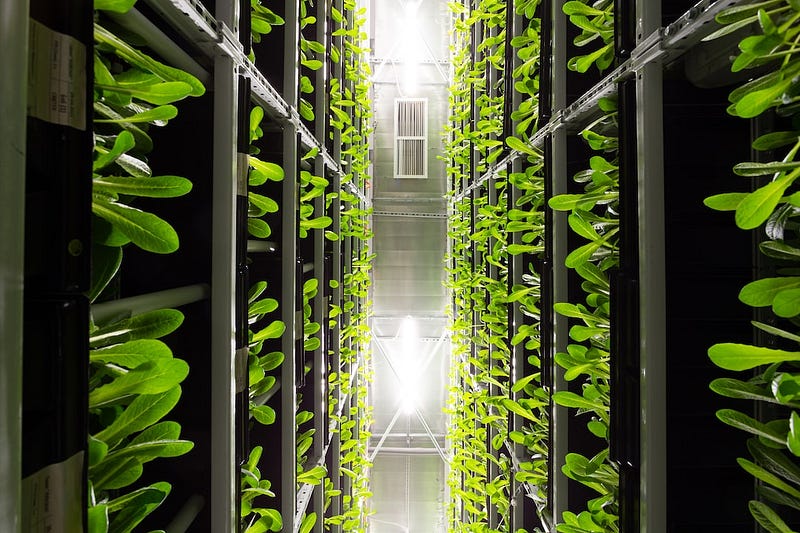
Section 2.1: The Rise of Vertical Farming
Vertical farming represents a transformative approach to agriculture, offering numerous advantages over traditional methods. This innovative farming technique can increase crop yields significantly while using 70%-95% less water. By utilizing underused spaces like rooftops or abandoned buildings, vertical farms are able to mitigate the issue of dwindling arable land caused by urbanization and industrial development.

Section 2.2: Mung Beans as a Sustainable Protein Source
In Southeast Asia, a staggering 77% of new plant-based meats introduced in 2022 primarily utilized wheat and soy sourced from the West. However, mung beans present a promising alternative that could diversify the region's protein offerings. These legumes can be utilized in various food categories, appealing to lactose-intolerant consumers and those with allergies to common ingredients like soy and wheat. Additionally, mung beans are a sustainable option, requiring less land and water than traditional animal-based proteins.

Lene Lange discusses the development of a sustainable and circular bioeconomy in the EU, emphasizing the role of alternative proteins in enhancing food security.
Section 2.3: Debunking Myths About Plant-Based Diets
A cardiologist has addressed ten common misconceptions surrounding plant-based diets, emphasizing their nutritional adequacy for all life stages, including athletic performance. With proper supplementation, individuals can obtain essential nutrients like vitamin B12 and vitamin D. Furthermore, plant-based diets can deliver omega-3 fatty acids, iron, calcium, and fiber, while dispelling myths about costs and health risks associated with such diets.

Chapter 3: The Future of Food Technology
Section 3.1: The Role of Precision Fermentation
An emerging trend in the food industry, precision fermentation, shows strong consumer interest. A significant 77% of US adults familiar with this technology are inclined to purchase products made through precision fermentation, highlighting its market potential. Younger generations, particularly Millennials and Gen Z, are especially keen on embracing new food technologies, favoring companies that prioritize sustainability and animal welfare.

In summary, the transformation towards a sustainable food system is underway, driven by innovative technologies and consumer awareness. As we navigate the complexities of food production and environmental impact, it is essential to educate consumers about the benefits of alternative proteins and sustainable practices.